Trichomoniasis: Causes, Symptoms, Testing & Treatment - Cleveland Clinic
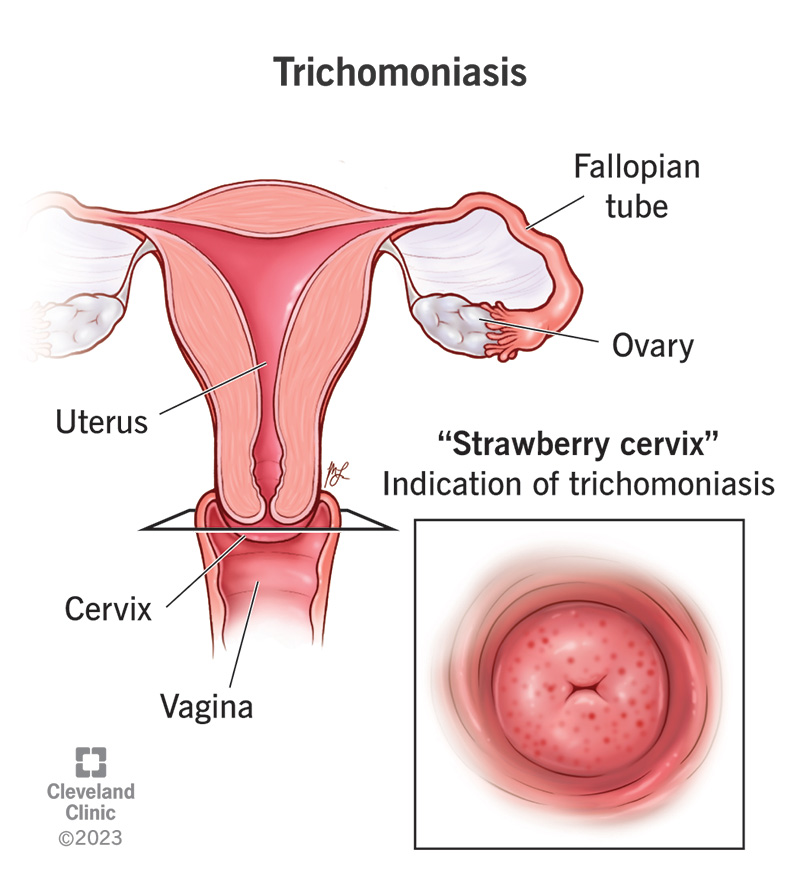
What are the symptoms of trichomoniasis?
One reason trich spreads so easily is that a large number of infected people — up to 70% — never have symptoms. You may infect others before you know you have the disease. When symptoms occur, they tend to appear within five to 28 days after exposure. Symptoms are more common in women or people AFAB. Researchers aren't entirely sure why some people have symptoms and others don't.
Signs of trichomoniasis in males and people assigned male at birth (AMAB)
Men and people AMAB rarely show signs of infection. In those who do, the most common are:
- Froth-like discharge from your penis.
- Burning after ejaculation or painful urination.
- Irritation or itching inside your penis.
Signs of trichomoniasis in females and people AFAB
Women and people AFAB tend to have more noticeable symptoms than men. Some of them are:
- Thin (or sometimes foamy) white, yellow or greenish vaginal discharge that has a bad odor.
- Irritation, soreness or redness around the opening of your vagina.
- Pain or discomfort during intercourse or when peeing.
What causes the condition?
A small parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis causes trich. Once you have the infection, you can give trich to someone else through:
- Vaginal-penile or vaginal-vaginal intercourse.
- Anal sex.
- Oral sex.
- Genital touching (skin-to-skin contact without ejaculation).
You can't spread trich by sharing food and drinks, kissing, holding hands or through other nonsexual forms of contact.
In addition to affecting your genitals, trich can also infect your anus, mouth and hands.
Can trichomoniasis be caused by poor hygiene?
No. Poor hygiene won't cause trichomoniasis. A parasite causes trich. The parasite spreads from partner to partner during sexual contact.
Can a UTI cause trichomoniasis?
No, a urinary tract infection (UTI) doesn't cause trichomoniasis.
Is trichomoniasis (trich) contagious?
Yes, trich is contagious. Many people aren't aware they have it and unknowingly spread it to their sexual partners.
Risk factors
Trich can affect anyone regardless of their assigned sex. Women and people AFAB are more likely to get trich. Your risk for trich increases if you:
- Don't use condoms while having sex.
- Have multiple sexual partners.
Complications of this condition
Untreated trich increases your risk of becoming infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) if you're exposed to the virus. Untreated HIV can lead to AIDS. Women and people AFAB who have trich and HIV are more likely to pass both diseases on to their partners. For this reason, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that HIV-positive women and people AFAB get tested for trich at least once a year.
Comments
Post a Comment